 Controlled Airspace
Controlled Airspace
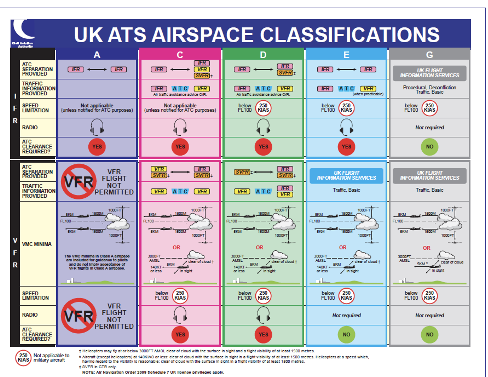
Airspace is organised into different classifications A-G. The characteristics of these, including the applicable VMC minima, are set by the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) and applied in Europe under SERA*. There are 5 classifications of controlled airspace (A-E) of which 4 are used in the UK: A, C, D and E. Further details on Controlled Airspace in the UK is found in the UK AIP en-route Section 1.4 (ENR1.4 ATS Airspace Classification and Description).
| Class A | |
|---|---|
| Where | Most airways and some TMAs |
| Flight Rules | IFR only. VFR flight not permitted |
| Clearance | ATC clearance required |
| Air Traffic Service | Air Traffic Control service |
| Separation | Separation between all flights |
| Class C | |
|---|---|
| Where | Mostly above FL195, some airways and some CTAs |
| Flight Rules | IFR and VFR permitted. In UK VFR flight is generally not permitted above FL195. Specific arrangements for glider operations in TRAs apply |
| Clearance | ATC clearance required |
| Air Traffic Service | Air Traffic Control service |
| Separation | Separation provided between IFR flights and between IFR flights and VFR flights. VFR flights are provided with traffic information. Traffic avoidance advice is available on request to VFR flights on other VFR flights. |
| Class D | |
|---|---|
| Where | Most aerodrome CTRs and CTAs. Some TMAs and lower levels of selected airways |
| Flight Rules | VFR flight permitted. SVFR permissible in CTRs. |
| Clearance | ATC clearance required |
| Air Traffic Service | Air Traffic Control service |
| Separation | Separation provided between IFR flights, between SVFR flights, and between IFR and SVFR flights. VFR flights are not provided with separation but are provided with traffic information. Traffic avoidance advice is available on request to IFR flights on VFR flights and to VFR flights on IFR and other VFR flights. |
| Class E | |
|---|---|
| Where | Some CTAs and Scottish airways |
| Flight Rules | IFR and VFR flight permitted. |
| Clearance | ATC clearance required for IFR flight. ATC clearance not required for VFR flight; pilots encouraged to contact ATC. |
| Air Traffic Service | Air Traffic Control Service provided to IFR flights and UK Flight Information Services are available to VFR flights. |
| Separation | Separation provided between IFR flights. VFR flights are not required to receive an Air Traffic Service and are not provided with separation. IFR flights may receive information on known VFR traffic. |
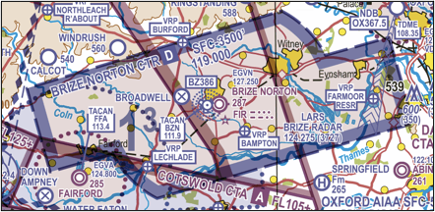
Control Zone (CTR)
These are established around aerodromes in the UK and extend from the surface to an upper altitude or level, with the shape orientated around the length of the most commonly used runway. In the UK they are normally Class D. They are marked on VFR charts with a blue broken border with blue tint along the inner edge (Figure 1).
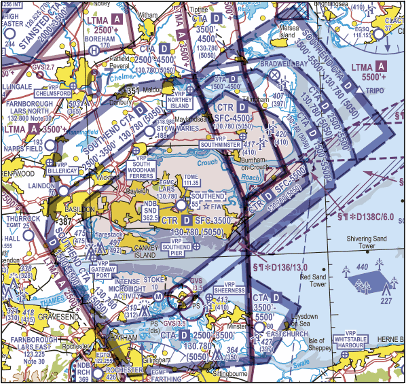
Control Area (CTA)
These normally overlay CTRs and extend further beyond the aerodrome. They normally start around 1,500 feet but this can vary. They are often Class D or Class E; however some higher or larger control areas are Class A or C. Pilots of VFR flights who wish to operate without receiving an Air Traffic Service within Class E airspace in an aircraft with a serviceable transponder, or within Class E airspace additionally notified as Transponder Mandatory Zone (TMZ) must display either:
- The VFR conspicuity code Mode A 7000 as a minimum with altitude reporting; (Mode C or S is preferred if equipped), or
- The appropriate Frequency Monitoring Code (FMC) for that volume of airspace.
CTA are marked on VFR charts with a blue broken border with a blue tint along the inner edge (Figure 2). A wide tint denoted the extremity of the CTA and a narrow tint denotes level changes within that area.
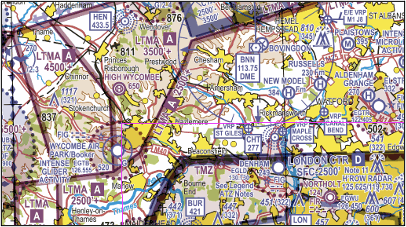
Terminal Control Area (TMA)
These cover areas where there may be several busy aerodromes close together; for example, the London, Manchester or Scottish TMAs. They are often Class A and marked on VFR charts with a magenta solid border with a magenta tint along the inner edge of the area when Class A (Figure 3), or blue for class D. A narrow tint denotes level changes within that area. A wide tint denoted the extremity of the controlled airspace, this may be the TMA edge OR the edge of any adjoining CTA.
Airways
These are CTAs that link different parts of the airspace structure together, in which mostly IFR traffic transits. They have designations consisting of letters and numbers. They are often Class A with some airways in Scotland being Class E combined with a Transponder Mandatory Zone (TMZ). They are marked on VFR charts with a magenta solid border with a magenta tint along the inner edge of the area if Class A (Figure 4). A wide tint denoted the extremity of the CTA and a narrow tint denotes level changes within that area. Class E airways are denoted with a dashed blue line accompanied by TMZ markings as appropriate (See TMZ section) Except where stated otherwise the width of an Airway is 5NM either side of a straight line joining each two consecutive points.
*From 1 January 2021 the UK law that applies to such aviation rights and obligations are the retained EU Regulations, as amended by various UK Statutory Instruments (made under the European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2018)

